Docker is a set of tools that utilises OS-level virtualization to running software in packages called container.
While Docker is mainly used in deployment, it can also be use in development environment. By running a container for development environment, we can avoid to install a bunch of tools or languages on our machine.
For example, we can use Docker to run service such as postgres and pgadmin for database service and administration platform for PostgreSQL respectively in a container.
To demonstrate, we will configure Postgres and pgAdmin with Docker Compose for database service for our development environment.
Table of contents
- Tools
- Create a Docker Compose file
- Running Docker Compose
- Open pgAdmin
- Stopping Docker Compose
- References
Tools
First, we need to install the tools required.
Both can be installed by referring to the official guide on how to install based on our machine platform.
Create a Docker Compose file
Docker Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. By using Docker Compose, we can orchestrate on how the applications/services start in the container by a single command.
Moreover, Docker Compose allows us to:
- Start, stop, and rebuild services
- View the status of running services
- Stream the log output of running services
- Run a one-off command on a service
Next, we are going to create a Docker Compose file docker-compose.yml to define the services that we are going to run in the container.
The services are:
- postgres: PostgreSQL database service
- pgadmin: Administration and development platform for PostgreSQL
postgres
Below is the snippet for the service:
postgres:
image: postgres:12.3-alpine
restart: always
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgres
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
volumes:
- postgres:/var/lib/postgresql/dataExplanation
image: Specify the image to start the container from. In this case, we are going to use postgres:12.3-alpine from Docker Hub.restart: Configure container to always restart if container stopped unexpectedly.environment: Configure environment variable for database superuser authentication.volumes: Mount named volumes for database files.
pgadmin
Below is the snippet for the service:
pgadmin:
image: dpage/pgadmin4:4.23
environment:
PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL: [email protected]
PGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD: password
PGADMIN_LISTEN_PORT: 80
ports:
- 15432:80
volumes:
- pgadmin:/var/lib/pgadmin
depends_on:
- postgresExplanation
image: Specify the image to start the container from. In this case, we are going to use dpage/pgadmin4:4.23 from Docker Hub.environment: Configure environment variable for application authentication and setup.ports: Map port between host machine 15432 and container 80.volumes: Mount named volumes for application files.depends_on: Define the dependencies of services. This allow us to deploy service in order; e.g.postgres->pgadmin.
Example
Then, we will going to put all services' configuration in file docker-compose.yml. Because we are using the named volume, we also need to configure the volumes based on the name we used in services.
Snippet
version: "3"
services:
postgres:
image: postgres:12.3-alpine
restart: always
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgres
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
volumes:
- postgres:/var/lib/postgresql/data
pgadmin:
image: dpage/pgadmin4:4.23
environment:
PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL: [email protected]
PGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD: password
PGADMIN_LISTEN_PORT: 80
ports:
- 15432:80
volumes:
- pgadmin:/var/lib/pgadmin
depends_on:
- postgres
volumes:
postgres:
pgadmin:Running Docker Compose
First, we are going to check and validate the Compose file by execute command: docker-compose config.
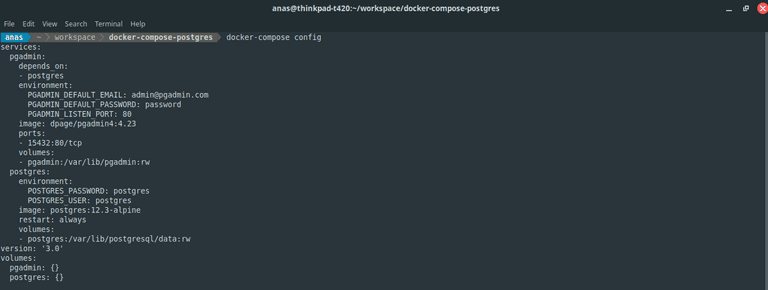 Figure 01: Example
Figure 01: Example docker-compose config output
Next, we are deploying and running the service by execute command: docker-compose up -d.
 Figure 02: Example
Figure 02: Example docker-compose up -d output
The output may vary depends on if we already downloaded the images and setup the volumes.
To check if services are running successfully, we can use command: docker-compose ps.
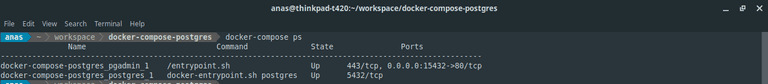 Figure 03: Example
Figure 03: Example docker-compose ps output
Open pgAdmin
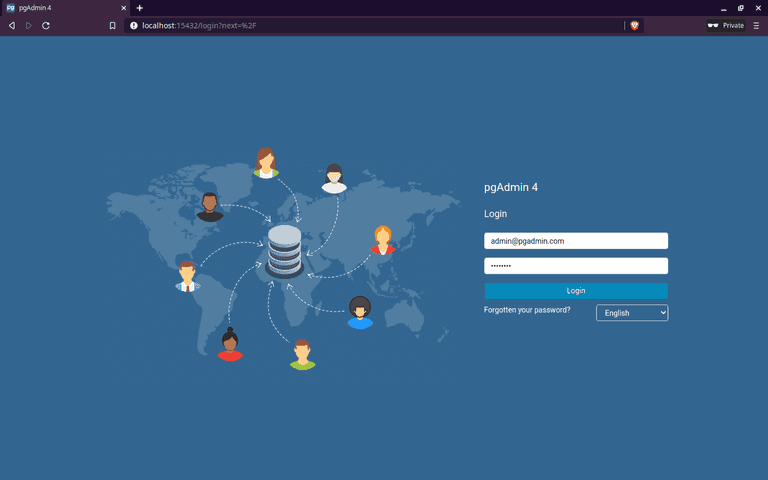
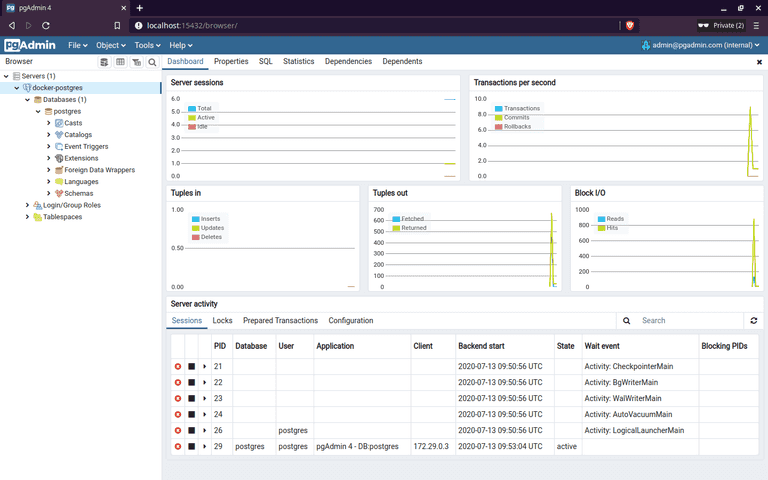
After running Docker Compose services, open web browser and go to localhost:15432. The port number is based on the mapping we configured under pgadmin service.
Then key-in the email and password configured using the environment variable: PGADMIN_DEFAULT_EMAIL and PGADMIN_DEFAULT_PASSWORD.
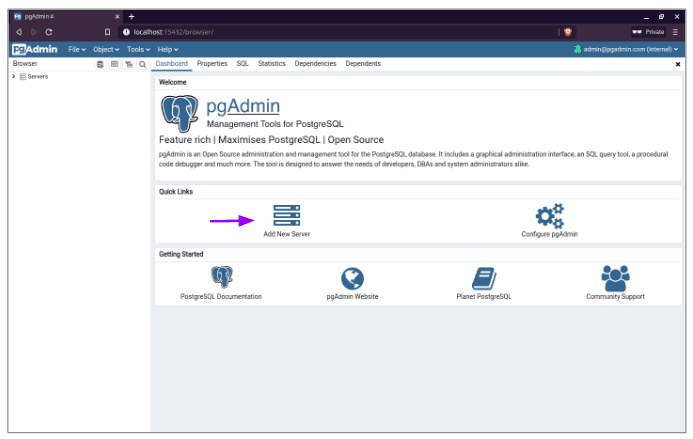
Setup database
Click Add New Server under Quick Links.
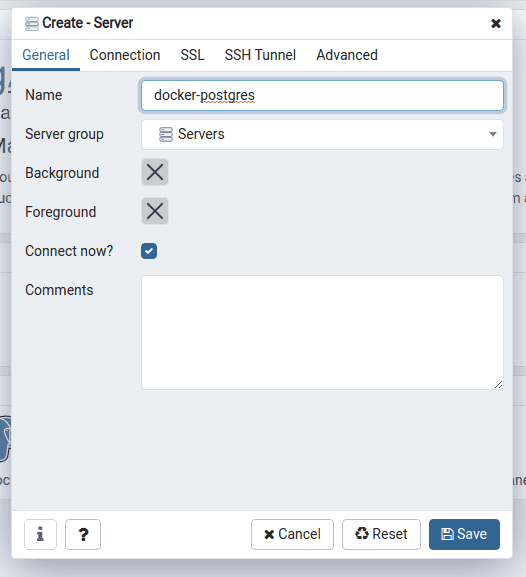
Enter Name under General. The value can be anything.
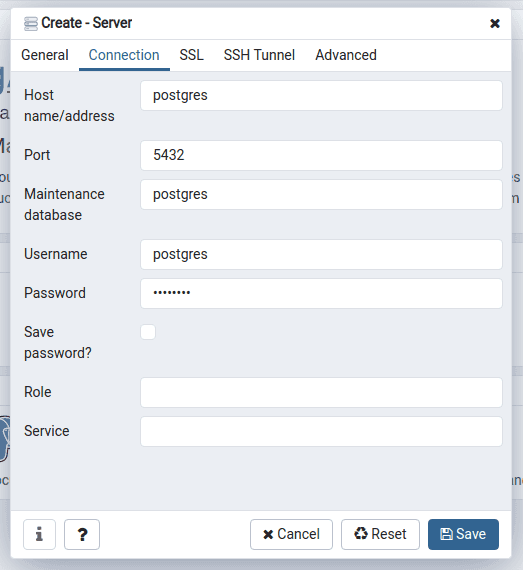
Enter Host name/address, Username and Password under Connection.
- For Host name/address, the value is the Docker Compose database service name, in our case is postgres.
- For Username, the value is the environment variable
POSTGRES_USER. - For Password, the value is the environment variable
POSTGRES_PASSWORD.
And click Save to finish create. After done, we can get access to the database from the sidebar.
Stopping Docker Compose
To stop Docker Compose service, just execute command: docker-compose down
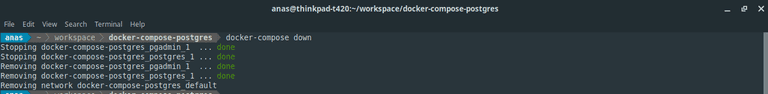 Figure 09: Example
Figure 09: Example docker-compose down output